Charging systems
Generalities
They serve to generate electrostatic charges on dielectric surfaces.
The purpose is to create electrostatic “bonding,” which is very useful in many fields of application. Power is supplied by a high-voltage DC generator, up to 60,000 V fìssa or adjustable.
The main industries of application are as follows:
- Plastics molding (in-mold labels; in-mouldlabeling)
- Metal sheet protection with plastic films
- Wood industry
- Packaging of books, magazines and objects with plastic film
Generators essentially contain current transformers and rectifiers, plus any regulation and monitoring systems.
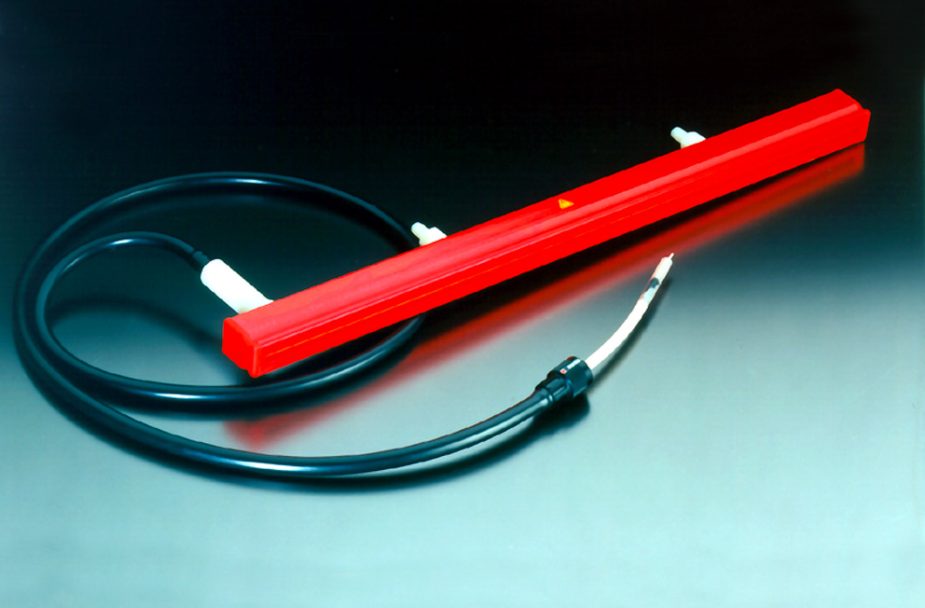
They can have 1, 2 or more outputs for as many charge bars. The charging bars consist of conductors embedded in resin and the charging tips. A suitably shielded high-voltage cable connects bar and generator. The bars act about 50 mm from the surface, under which a grounded counter electrode must be placed. Charging bars are not safe to touch, and indeed, one should avoid placing them in a position easily reached by operators. In fact, energy can short-circuit through a part of the human body, generating an electric arc.
The resulting discharge does not cause serious damage but is painful. Direct current, varying from 25000 to 60000 V, feeds the conductor intemo to the bar to which the charging tips are electrically connected. A stationary electric field is generated between the bar and counterelectrode with parallel lines of force running from the tips to the counterelectrode. By interposing a dielectric surface in this electric field, surface molecules become polarized. If there are two contacting surfaces, the polarization realizes electrostatic bonding. It is important that the tips do not directly face the counter electrode otherwise a short circuit with electric arc is realized and the rod will not work. Polarization of molecules does not have an infinite duration, so over time the charge tends to decrease especially in the presence of moisture in the air or in the material being treated (e.g. paper).
In general, ambient humidity greatly reduces electrostatic charges on materials.
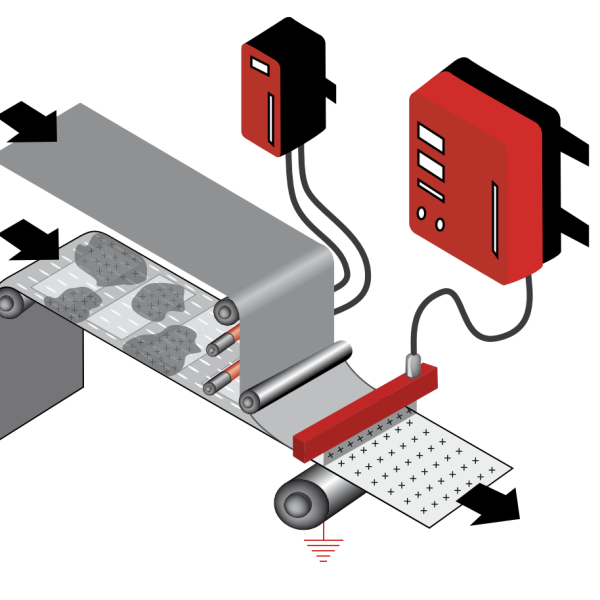
A charge bar connected to a high-voltage generator is used to electrostatically “glue” two films together. A grounded metal counter electrode should be placed under the bar. The efficiency of charging increases if an ionizing bar is installed upstream to make the surface neutral.
Available charging systems
The basic components are:
- A high-voltage charge generator;
- A charging rod or electrode;
- A high-voltage cable;
It is strongly recommended to make the material neutral by discharging it electrostatically before subjecting it to charging. Various types of electrodes and charge bars are available, but it is important to know that they always require a counter electrode. If a grounded metal counter electrode is not available, a discharge bar can be used for this function.
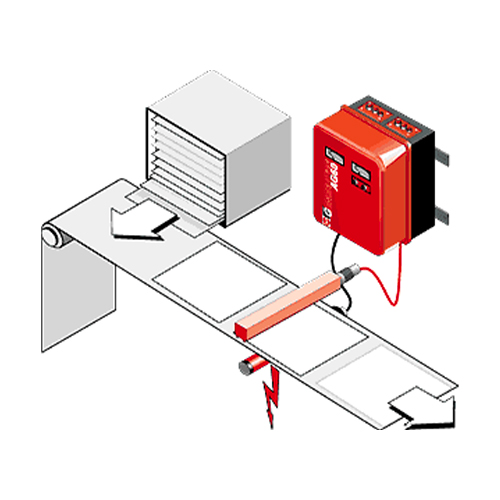
Charge generators
These are generators that provide a positive or negative output voltage, of various powers and devices depending on the models. They are used in conjunction with HAUG charge bars and related counterelectrodes to achieve electrostatic bonding between two materials. Typical applications are in the packaging industry, plastic coatings, glass and electrical industries.
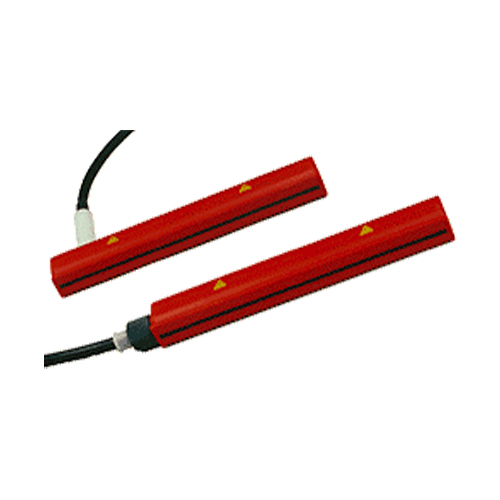

ALS Charge Bars
Electrostatic charge is applied by means of charging rods or electrodes. This charge can be positive or negative depending on the generator to which the bar is connected. The high-voltage cable connected with the generator can have an axial or radial connectio There are models for high temperatures (up to +130C).
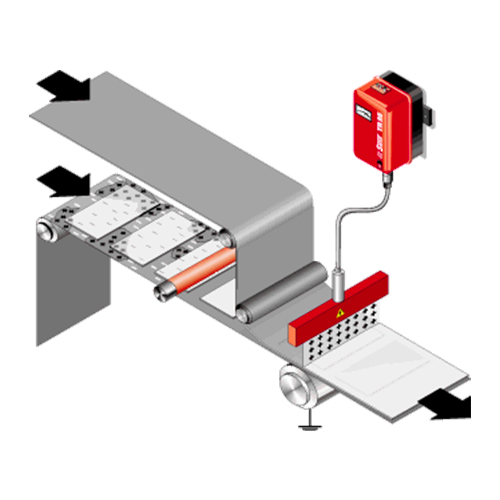
Tristat TR25 Triode Charging Systems
This charge generator can be connected to electrodes or charge bars having triode technology. It has 1 output of max 22Kvolt (positive or negative), voltage is output adjustable, has analog display. Charging can be pulse-controlled. The main feature is to work with a very stable output voltage, and to have a very high current that allows installation of the electrode very close to the surface to be treated without harmful sparks occurring. The triode electrode has 2 metal side plates grounded through the connection with the generator, and this allows for a particularly concentrated and effective discharge.
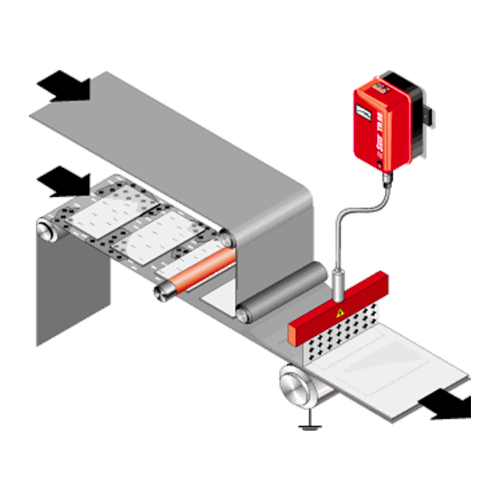
Tristat TR15 triode charging systems
This charge generator can be connected to electrodes or charge bars having triode technology. It has 1 output of max 22Kvolt positive or negative. The main feature of this technology is to work with a very stable output voltage, and to have a very high current that allows installation of the electrode very close to the surface to be treated without harmful sparks occurring. The triode electrode has 2 metal side plates grounded through the connection with the generator, and this allows a particularly concentrated and effective discharge.
Do you want to request an offer?
Are you interested in receiving more information and being contacted by one of our specialized operators?
Request your offer now

Do you want to request an offer?
Are you interested in receiving more information and being contacted by one of our specialized operators?
Request your offer now
Frequently asked questions
What is electrostatics?
Electrostatics studies stationary electric fields, that is, generated by static charges arranged on dielectric surfaces.
What can be done with electrostatic systems?
One can eliminate the unwanted charge or one can generate a charge.
What is meant by ionization?
It is equivalent to the elimination of electrostatic charge. A bar produces ions that remove charges on the surface.
In what cases should a surface be loaded?
The most typical case is to make one surface adhere to another, making a kind of electrostatic “bonding.”
Are discharge and charge technically different processes?
Yes, a discharge (ionizing) bar generates ions while a charge bar generates a stationary electric field.
If I want to download a movie, can I use one ion bar?
No, since the charges on a dielectric are stationary it is necessary to discharge both faces of the film via two opposing bars.
Why not more simply use an anti-static brush?
This is a good solution to REDUCE the charge, but if you need to ELIMINATE the charge you must use an ionizing bar.
Up to what distance does a discharge bar act?
20-30 mm. However, with the help of appropriate compressed or ventilated air systems, it is possible to reach 500 mm and more.
Are there injury risks in the use of electrostatic systems?
Discharge (ionizing) bars are safe to the touch and do not give any problems (excluding special reported cases). The charge bars, on the other hand, should not be touched during operation; in fact, they should be shielded.
How can I verify the effectiveness of an electrostatic treatment?
Numerous electrostatic charge measurement systems are available in the catalog, but generally the result is seen immediately after treatment.







